Copper Dissolution Rate of Modified Self-Polishing Antifouling Paint with Cerium Oxide
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55981/jsmi.2025.8753Keywords:
Self-polishing, Antifouling, Biofouling, SeaNine 211, Cerium oxide, Leached-out testAbstract
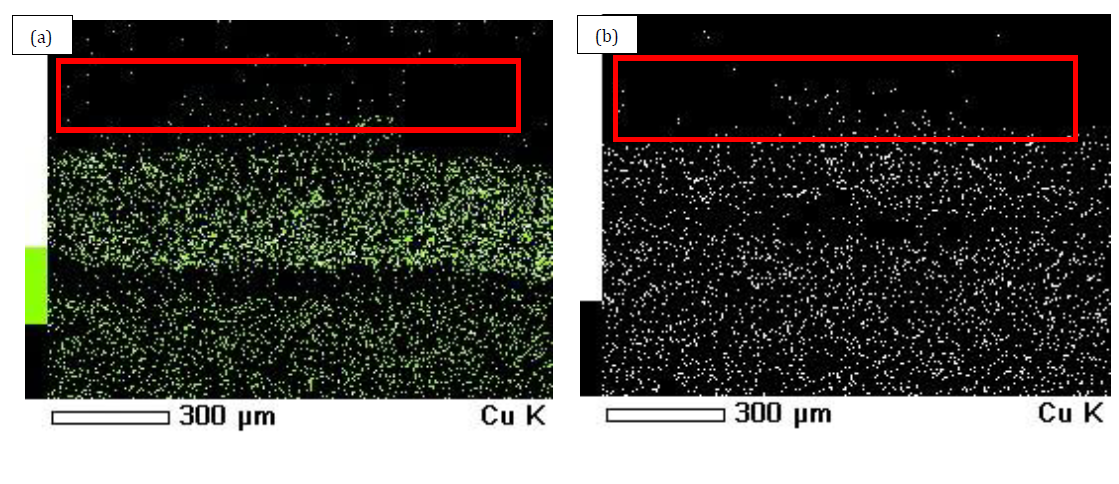
The main objective of the work is to substitute SeaNine 211 in self-polishing antifouling (SPA) paint formulations for marine coating using cerium oxide as a co-biocide. The development of SPA paint with cerium oxide as a co-biocide is expected to significantly improve the environmental friendliness and efficacy of antifouling paints. The preparation of modified SPA paint was undertaken by incorporating the cerium oxide with various concentrations (0.1, 0.3, and 0.5 wt.%) in the SPA paint formulation without SeaNine 211. The copper dissolution rate determines the efficacy of antifouling paint, where the greater the copper release rate, the greater the efficacy of the antifouling paint. The leached-out test results obtained suggest that with an increase of 0.1% wt in the concentration of cerium oxide, there was an improvement in the copper dissolution rate. It was also observed that the mild steel specimens were coated with modified SPA paint when immersed in the seawater for 7 days for testing. The properties were observed by utilizing scanning electron microscopy (SEM). An improvement in the copper dissolution rate was found, as shown by cerium oxide SPA paint when contrasted with bare paint. The contact angle test finding also suggests that adding 0.1% wt of cerium oxide to the SPA paint will increase the dissolution rate of copper. This work could provide insight into developing an environmentally friendly antifouling paint co-biocide.
Downloads
References
[1] Y. A. A. Soliman, A. M. Brahim, A. H. Moustafa, and M. A. F. Hamed. "Antifouling evaluation of extracts from Red Sea soft corals against primary biofilm and biofouling." Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed., vol. 7, no. 11, pp. 991-997, 2017.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apjtb.2017.09.016
[2] G. Gizer, U. Önal, M. Ram, and N. Sahiner. "Biofouling and Mitigation Methods: A Review." Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem., vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 1-25, 2023.
https://doi.org/10.33263/BRIAC132.185
[3] J. F. Lindgren, E. Ytreberg, A. Holmqvist, M. Dahlstrom, P. Dahl, M. Berglin, A. -L. Wrange, and M. Dahlstrom. "Copper release rate needed to inhibit fouling on the west coast of Sweden and control of copper release using zinc oxide." Biofouling, vol. 34, no. 4, pp. 453-463, 2018.
https://doi.org/10.1080/08927014.2018.1463523
[4] I. Davidson, P. Cahill, A. Hinz, D. Kluza, C. Scianni, and E. Georgiades. "A Review of Biofouling of Ships' Internal Seawater Systems." Front. Mar. Sci., vol. 8, no. October, pp. 1-16, 2021.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2021.761531
[5] P. Wang, D. Zhang, and Z. Lu. "Slippery liquid-infused porous surface bio-inspired by pitcher plant for marine anti-biofouling application." Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces, vol. 136, pp. 240-247, 2015.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2015.09.019
[6] N. Hadžić, I. Gatin, T. Uroić, and V. Ložar. "Biofouling dynamic and its impact on ship powering and dry-docking." Ocean Eng., vol. 245, no. January, 2022.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.110522
[7] M. Hu, K. Korschelt, M. Viel, N. Wiesmann, M. Kappl, J. Brieger, K. Landfester, H. Therien-Aubin, and W. Tremel. "Nanozymes in Nanofibrous Mats with Haloperoxidase-like Activity to Combat Biofouling." ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, vol. 10, no. 51, pp. 44722-44730, 2018.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b16307
[8] P. A. Turley, R. J. Fenn, and J. C. Ritter. "Pyrithiones as antifoulants: Environmental chemistry and preliminary risk assessment." Biofouling, vol. 15, no. 1-3, pp. 175-182, 2000.
https://doi.org/10.1080/08927010009386308
[9] T. V. Raveendran and V. P. L. Mol. "Natural product antifoulants." Curr. Sci., vol. 97, no. 4, pp. 508-520, 2009.
[10] N. Voulvoulis, M. D. Scrimshaw, and J. N. Lester. "Comparative environmental assessment of biocides used in antifouling paints." Chemosphere, vol. 47, no. 7, pp. 789-795, 2002.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(01)00336-8
[11] D. M. Yebra. "Antifouling technology - Past, present and future steps towards efficient and environmentally friendly antifouling coatings." Progress in Organic Coatings, vol. 50, no. 2. pp. 75-104, 2004.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2003.06.001
[12] N. Voulvoulis, M. D. Scrimshaw, and J. N. Lester. "Alternative antifouling biocides." Appl. Organomet. Chem., vol. 13, no. 3, pp. 135-143, 1999.
https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-0739(199903)13:3<135::AID-AOC831>3.0.CO;2-G
[13] E. Almeida, T. C. Diamantino, and O. de Sousa. "Marine paints: The particular case of antifouling paints." Prog. Org. Coatings, vol. 59, no. 1, pp. 2-20, 2007.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2007.01.017
[14] N. Voulvoulis. "Comparative environmental assessment of biocides used in antifouling paints." Chemosphere, vol. 47, no. 7, pp. 789-795, 2002.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(01)00336-8
[15] L. Chen and J. C. W. Lam. "SeaNine 211 as antifouling biocide: A coastal pollutant of emerging concern." J. Environ. Sci. (China), vol. 61, pp. 68-79, 2017.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2017.03.040
[16] J. W. Do, M. N. Haque, H. -J. Lin, B. H. Min, D. -H. Lee, J. -H, Kang, M. K. Kim, J. -H. Jung, and J. -S. Rhee. "Constant exposure to environmental concentrations of the antifouling biocide Sea-Nine retards growth and reduces acetylcholinesterase activity in a marine mysid." Aquat. Toxicol., vol. 205, no. October, pp. 165-173, 2018.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2018.10.019
[17] T. Onduka, D. Ojima, M. Ito, K. Ito, K. Mochida, and K. Fujii. "Toxicity of the antifouling biocide Sea-Nine 211 to marine algae, crustacea, and a polychaete." Fish. Sci., vol. 79, no. 6, pp. 999-1006, 2013.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-013-0678-6
[18] Y. Su, H. Li, J. Xie, C. Xu, Y. Dong, F. Han, J. G. Qin, L. Chen, and E. Li. "Toxicity of 4,5-dichloro-2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one (DCOIT) in the marine decapod Litopenaeus vannamei." Environ. Pollut., vol. 251, pp. 708-716, 2019.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.05.030
[19] L. Chen, J. Sun, H. Zhang, D. W. T. Au, P. K. S. Lam, W. Zhang, V. B. Bajic, J. -W. Qiu, and P. -Y. Qian. "Hepatic proteomic responses in marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma) chronically exposed to antifouling compound butenolide [5-octylfuran-2(5H)-one] or 4,5-dichloro-2- n -octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-One (DCOIT)." Environ. Sci. Technol., vol. 49, no. 3, pp. 1851-1859, 2015.
https://doi.org/10.1021/es5046748
[20] I. Wendt, T. Backhaus, H. Blanck, and Å. Arrhenius. "The toxicity of the three antifouling biocides DCOIT, TPBP and medetomidine to the marine pelagic copepod Acartia tonsa." Ecotoxicology, vol. 25, no. 5, pp. 871-879, 2016.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-016-1644-8
[21] Y. Su, H. Li, C. Xu, X. Wang, J. Xie, J. G. Qin, L. Chen, and E. Li. "Endoplasmic reticulum stress mediates 4,5-dichloro-2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one (DCOIT)-induced toxicity and liver lipid metabolism changes in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus)," Environ. Pollut., vol. 242, pp. 1981-1987, 2018.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.07.046
[22] M. Zhang, C. Zhang, X. Zhai, F. Luo, Y. Du, and C. Yan. "Antibacterial mechanism and activity of cerium oxide nanoparticles." Sci. China Mater., vol. 62, no. 11, pp. 1727-1739, 2019.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s40843-019-9471-7
[23] R. Wu, W. Wang, Q. Luo, X. Zeng, J. Li, Y. Li, Y. Li, J. Li, and N. Wang. "Room temperature synthesis of defective cerium oxide for efficient marine anti-biofouling." Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater., no. 0123456789, 2021.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00256-7
[24] N. Wang, W. Li, Y. Ren, J. Duan, X. Zhai, F. Guan, L. Wang, and B. Hou. "Investigating the properties of nano core-shell CeO2@C as haloperoxidase mimicry catalyst for antifouling applications." Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp., vol. 608, no. September 2020, p. 125592, 2021.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125592
[25] K. Herget, P. Hubach, S. Pusch, P. Deglmann, H. Gotz, T. E. Gorelik, I. A. Gural'skiy, F. Pfitzner, T. Link, S. Schenk, M. Panthofer, V. Ksenofontov, U. Kolb, T. Opatz, R. Andre, and W. Tremel. "Haloperoxidase Mimicry by CeO2−x Nanorods Combats Biofouling," Adv. Mater., vol. 29, no. 4, pp. 1-8, 2017.
https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201603823
[26] R. Coatings. "Standard Test Method for Copper Release Rates Determination of Copper Release Rate From Antifouling Coating Systems in Artificial Seawater 1." Test, vol. 06, no. February 2000, pp. 1-8, 2003.
[27] A. O. Valkirs, P. F. Seligman, E. Haslbeck, and J. S. Caso. "Measurement of copper release rates from antifouling paint under laboratory and in situ conditions : implications for loading estimation to marine water bodies." vol. 46, pp. 763-779, 2003.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-326X(03)00044-4
[28] M. Lagerström, J. F. Lindgren, A. Holmqvist, M. Dahlström, and E. Ytreberg. "In situ release rates of Cu and Zn from commercial antifouling paints at different salinities." Mar. Pollut. Bull., vol. 127, no. December 2017, pp.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.12.027
[29] E. Ytreberg. "Comparison of toxicity and release rates of Cu and Zn from anti-fouling paints leached in natural and artificial brackish seawater." Sci. Total Environ., vol. 408, no. 12, pp. 2459-2466, 2010.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.02.036
[30] L. G. Ecco, M. Fedel, F. Deflorian, J. Becker, B. B. Iversen, and A. Mamakhel. "Waterborne acrylic paint system based on nanoceria for corrosion protection of steel," Prog. Org. Coatings, vol. 96, pp. 19-25, 2016.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2016.02.010
[31] H. Zhang, J. Cao, L. Sun, F. Kong, J. Tang, X. Zhao, Y. Tang, and Y. Zuo. "Comparative Study on the Degradation of Two Self-Polishing Antifouling Coating Systems with Copper-Based Antifouling Agents." Coatings, vol. 12, no. 8, 2022, doi: .
https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12081156
[32] A. Matin, U. Baig, M. A. Gondal, S. Akhtar, and S. M. Zubair. "Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic surfaces prepared by spray-coating of facile synthesized Cerium(IV) oxide nanoparticles for efficient oil/water separation." Appl. Surf. Sci., vol. 462, no. April, pp. 95-104, 2018.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.08.104
[33] D. M. Yebra, S. Kiil, and K. Dam-Johansen. "Antifouling technology - Past, present and future steps towards efficient and environmentally friendly antifouling coatings." Prog. Org. Coatings, vol. 50, no. 2, pp. 75-104, 2004.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Arini Nikitasari, Januar Irawan, Gadang Priyotomo, J.W. Soedarsono, Rini Riastuti

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.