Surface Modification of Hematite using Stearic Acid as Hydrophobic Inorganic Pigment Materials
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55981/jsmi.2025.8982Keywords:
Hematite, Hydrophobic, Inorganic, Pigment, StearicAbstract
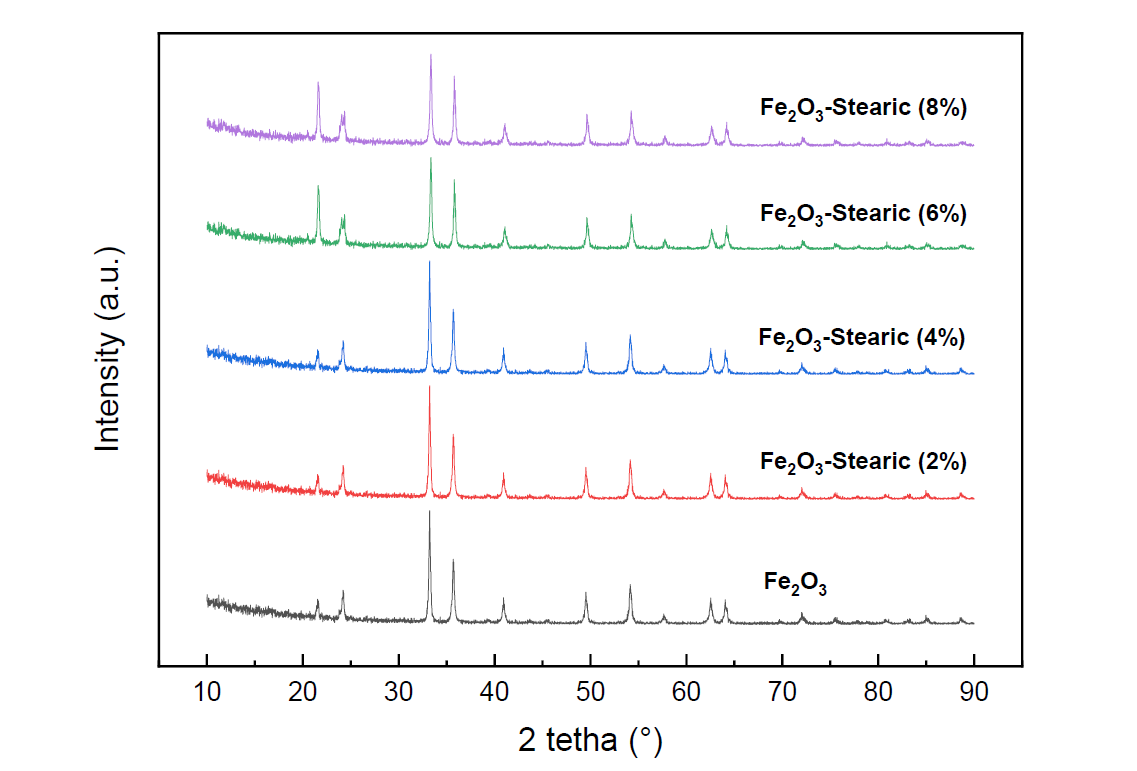
The inorganic pigment is a material that determines the color of a paint that can be used as a coating material. Until now, the basic material for red pigment, namely hematite, has been imported to meet domestic needs. This study aims to develop a hematite-based inorganic pigment material from the mill-scale waste of PT Krakatau Steel by modifying the surface to be hydrophobic, making the pigmenting material resistant to acid attack and preventing peeling and corrosion of the material. The surface modification of hematite is carried out by reacting it with stearic acid into ethanol as a solvent. Hematite was immersed in a stearic acid solution with various concentrations of 2, 4, 6, and 8% for 6 hours; it was then separated by filtration and followed by the drying process. The hematite-stearic was characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR), scanning electron microscope (SEM), and water contact angle (WCA). The results show that the grafting process successfully changed the properties of hematite to hydrophobic. It is also supported by the FTIR spectrum due to the presence of molecular vibration of C-H, C=O, C-O, and Fe-O. Then, the higher contact angle is 150.474° for the stearic acid concentration of 6%.
Downloads
References
[1] D. S. Khaerudini, I. Chanif, D. R. Insiyanda, F. Destyorini, S. Alva, and A. Pramono. "Preparation and characterization of mill scale industrial waste reduced by Biomass-Based carbon." Journal of Sustainable Metallurgy, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 510-518, 2019.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-019-00241-x
[2] D. A. P. Wardani, L. Rosmainar, R. M. Iqbal, and S. N. Simarmata. "Synthesis and characterization of magnetic adsorbent based on Fe2O3-fly ash from Pulang Pisau's power plant of Central Kalimantan." IOP Conference Series Materials Science and Engineering, vol. 980, no. 1, p. 012014, 2020.
https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/980/1/012014
[3] D. Mehta, S. Mazumdar, and S. K. Singh. "Magnetic adsorbents for the treatment of water/wastewater-A review." Journal of Water Process Engineering, vol. 7, pp. 244-265, 2015.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2015.07.001
[4] R. M. Iqbal, S. D. Nurherdiana, D. Hartanto, M. H. D. Othman, and H. Fansuri. "Morphological control of La0.7Sr0.3Co0.2Fe0.8O3-δ and La0.7Sr0.3MnO3-δ catalytic membrane using PEG-H2O additive." IOP Conference Series Materials Science and Engineering, vol. 348, p. 012008, 2018.
https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/348/1/012008
[5] R. M. Iqbal, E. P. Toepak, D. A. P. Wardani, E. Alyatikah, S. C. Angga, and L. Hakim. "Study of microstructure and optical properties of Fe2O3/TiO2 composites as functional materials." Jurnal Ilmiah Berkala Sains Dan Terapan Kimia, vol. 16, no. 2, p. 110, 2022.
https://doi.org/10.20527/jstk.v16i2.12142
[6] S. D. Nurherdiana. "Effect of the sintering process on the morphology and mechanical properties of La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3-Δ asymmetric flat membranes prepared by the phase inversion method." Ceramics - Silikaty, pp. 305-314, 2019.
https://doi.org/10.13168/cs.2019.0025
[7] W. P. Utomo, A. S. Wijayanti, S. D. Nurherdiana, R. M. Iqbal, D. Hartanto, and H. Fansuri. "Preparation and Morphological Property of Co3O4/BaxSr1-xCo0.8Fe0.2O3-δ (x=0.5-0.7) Membranes using Starch as Binder Agent." IOP Conference Series Materials Science and Engineering, vol. 588, no. 1, p. 012040, 2019.
https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/588/1/012040
[8] R. M. Iqbal, S. D. Nurherdiana M. S. Sahasrikirana, L. Harmelia, W. P. Utomo, E. P. Setyaningsih, and H. Fansuri. "The compatibility of NiO, CeO2, and NiO-CeO2 as a coating on La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3-Δ, La0.7Sr0.3Co0.2Fe0.8O3-Δ and La0.7Sr0.3Mn0.3O3-Δ Ceramic membranes and their mechanical properties." IOP Conference Series Materials Science and Engineering, vol. 367, p. 012032, 2018.
[9] N. Han, R. Chen, T. Chang, L. Li, H. Wang, and L. Zeng. "A novel lanthanum strontium cobalt iron composite membrane synthesized through beneficial phase reaction for oxygen separation." Ceramics International, vol. 45, no. 15, pp. 18924-18930, 2019.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.06.128
[10] N. Nurdini, Moh. M. Ilmi, E. Maryanti, P. Setiawan, G. T. M. Kadja, and N. Ismunandar. "Thermally-induced color transformation of hematite: insight into the prehistoric natural pigment preparation." Heliyon, vol. 8, no. 8, p. e10377, 2022.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10377
[11] Q. Yu, Y. L. Ke, X. K. Tan, G. D. Luo, S. B. Han, L. Yu, and G. Q. Luo. "Study on Surface Modification of Mica Pearl Pigment with Stearic Acid." Materials Science Forum, vol. 852, pp. 774-781, 2016.
https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.852.774
[12] A. Patti, H. Lecocq, A. Serghei, D. Acierno, and P. Cassagnau. "The universal usefulness of stearic acid as surface modifier: applications to the polymer formulations and composite processing." Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, vol. 96, pp. 1-33, 2021.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2021.01.024
[13] M. Hosseini-Zori, E. Taheri-Nassaj, and A. R. Mirhabibi. "Effective factors on synthesis of the hematite-silica red inclusion pigment." Ceramics International, vol. 34, no. 3, pp. 491-496, 2007.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2006.11.012
[14] Z. Cao, M. Daly, L. Clemence, L. M. Geever, I. Major, C. L. Higginbotham, and D. M. Devine. "Chemical surface modification of calcium carbonate particles with stearic acid using different treating methods." Applied Surface Science, vol. 378, pp. 320-329, 2016.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.03.205
[15] N. Xu, D. K. Sarkar, X. G. Chen, H. Zhang, and W. Tong. "Superhydrophobic copper stearate/copper oxide thin films by a simple one-step electrochemical process and their corrosion resistance properties." RSC Advances, vol. 6, no. 42, pp. 35466-35478, 2016.
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA01944G
[16] T. W. Manurung, S. U. M. Beladona, Muh. S. Hakim, L. Tesalonika, R. A. Al-Hadi, and R. M. Iqbal. "Surface modification of fly ash from asam-asam coal power plant using stearic acid as hydrophobic inorganic material." Jurnal Kimia Riset, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 59-68, 2024.
https://doi.org/10.20473/jkr.v9i1.57370
[17] F. Shafiq, C. Liu, H. Zhou, H. Chen, S. Yu, and W. Qiao. "Stearic acid-modified hollow hydroxyapatite particles with enhanced hydrophobicity for oil adsorption from oil spills." Chemosphere, vol. 348, p. 140651, 2023.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.140651
[18] R. M. Iqbal, M. H. D. Othman, M. A. Mokhter, D. S. Khaerudini, F. H. Abdullah, M. H. Puteh, J. Jaafar, and M. A. Rahman. "Innovative nonfluorinated-omniphobic membranes using palmitic acid surface grafting for efficient low-pressure desalination via membrane distillation." Chemical Papers, 2025.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-025-03882-3
[19] T. Tatarchuk, A. Shyichuk, N. Danyliuk, I. Lapchuk, and W. Macyk. "Water disinfection using hydrogen peroxide with fixed bed hematite catalyst - kinetic and activity studies." Environmental Science and Pollution Research, vol. 31, no. 18, pp. 26592-26605, 2024.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32794-0
[20] J. Vishnu, K. Praveenkumar, A. A. Kumar, A. Nair, R. Arjun, V. G. Pillai, B. Shankar, K. V. Shankar. "Multifunctional zinc oxide loaded stearic acid surfaces on biodegradable magnesium WE43 alloy with hydrophobic, self-cleaning and biocompatible attributes." Applied Surface Science, vol. 680, p. 161455, 2024.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2024.161455
[21] A. Patti, H. Lecocq, A. Serghei, D. Acierno, and P. Cassagnau. "The universal usefulness of stearic acid as surface modifier: applications to the polymer formulations and composite processing." Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, vol. 96, pp. 1-33, 2021.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2021.01.024
[22] Y. Zhang, Z. Zhang, J. Yang, Y. Yue, and H. Zhang. "A review of recent advances in superhydrophobic surfaces and their applications in drag reduction and heat transfer." Nanomaterials, vol. 12, no. 1, p. 44, 2021.
https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12010044
[23] S. Sun, H. Ding, and H. Zhou. "Preparation of TiO2-coated barite composite pigments by the hydrophobic aggregation method and their structure and properties." Scientific Reports, vol. 7, no. 1, 2017.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-10620-7
[24] S. Sun, H. Ding, X. Hou, D. Chen, S. Yu, H. Zhou, and Y. Chen. "Effects of organic modifiers on the properties of TiO2-coated CaCO3 composite pigments prepared by the hydrophobic aggregation of particles." Applied Surface Science, vol. 456, pp. 923-931, 2018.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.06.185
[25] C. A. Thennakoon, R. B. S. D. Rajapakshe, A. U. Malikaramage, and R. M. G. Rajapakse. "Factors affecting the hydrophobic property of stearic acid Self-Assembled on the TiO2 substrate." ACS Omega, vol. 7, no. 51, pp. 48184-48191, 2022.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Rendy Muhamad Iqbal, Retno Agnestisia, Akhmad Damsyik, Tiara Cristy Agatha Sinaga, Deni Shidqi Khaerudini, Ika Octavia Wulandari, Indri Susanti, Riandy Putra, F. Adany

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.