Color and Total Organic Carbon (TOC) Removal from Peat Water Using The Electrocoagulation Process: Central Composite Design for Optimization
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55981/jsmi.2025.9027Keywords:
Central composite design, Electrocoagulation, Peat water, Color removal, TOC removalAbstract
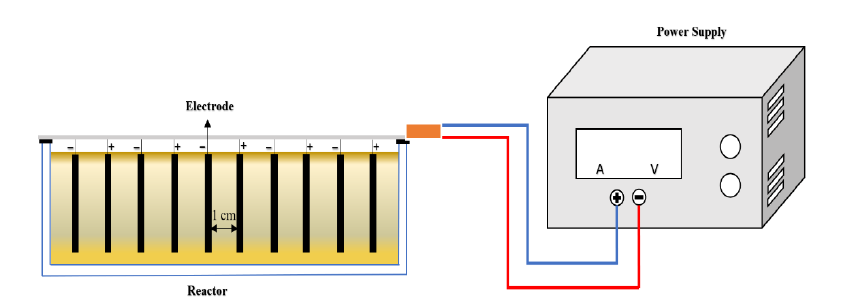
The electrocoagulation process is simple and environmentally friendly. It removes pollutants in peat water such as color and total organic carbon (TOC). In this study, the electrocoagulation process was designed, optimized, and investigated using central composite design (CCD) type response surface methodology (RSM). The effects of current density and reaction time in the range of 6–14 mA/cm2 and 30–90 minutes on the efficiency of color and TOC treatment were evaluated. The best results for removing output efficiency were 10 mA/cm2 for 30 minutes (98.1% color) and 10 mA/cm2 for 30 minutes (91% TOC). By comparing actual and predicted data, the optimum condition in this process occurs when the current density is 6.140 mA/cm2 and the reaction time is 76.042 minutes. The experimental data can be well described using the central composite design
Downloads
References
[1] N. A. Rahman, A. A. Linus, C. J. Jol, N. S. A. Jalal, C. K. Ming, W. W. S. W. Borhan, N. Baharuddin, S. N. A. Samsul, and N. A. Mutalip. "Kinetic modelling of peat water treatment with continuous electrocoagulation using aluminum electrodes." Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, vol. 11, no. 3, p. 109559, 2023.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2023.109559
[2] E. Aguilar-Ascón, L. Marrufo-Saldaña, and W. Neyra-Ascón. "Enhanced chromium removal from tannery wastewater through electrocoagulation with iron electrodes: Leveraging the Box-Behnken design for optimization." Heliyon, vol. 10, no. 3, p. e24647, 2024.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24647
[3] K. Khayan, A.H. Sutomo, A. Rasyid, W.L. Puspita, D. Hariyadi, T. Anwar, S. Wardoyo, R. Sahknan, and A. Aziz. "Integrated Water Treatment System for Peat Water Treatment." CLEAN - Soil, Air, Water, vol. 50, no. 2, p. 2100404, 2022.
https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.202100404
[4] N.A. Rahman, C. Jose Jol, A. Albania Linus, F.L. Dampam, N.S. Abdul Jalal, N. Baharudin, and W.W.S. Wan Borhan. "Desalination of Borneo tropical brackish peat water with adsorption process in continuous electrocoagulation treatment." Desalination, vol. 527, p. 115574, 2022.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2022.115574
[5] J. Muhammad. "Peat Water Purification by Hybrid of Slow Sand Filtration and Coagulant Treatment." Journal sof Environmental Science and Technology, vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 22-28, 2020.
https://doi.org/10.3923/jest.2020.22.28
[6] Y. Zevi, M. Qadafi, and S. Notodarmojo. "The Presence of Trihalomethanes and Haloacetic Acids in Tropical Peat Water." Journal of Engineering and Technological Sciences, vol. 54, no. 3, p. 220314, 2022.
https://doi.org/10.5614/j.eng.technol.sci.2022.54.3.14
[7] N. A. Rahman, A. A. Linus, E. E. Jihed, U. J. Gilan, N. K. M. F. Kumar, A. Phillip, A. Yassin, and A. Parabi. "Experimental Studies on Continuous Electrocoagulation Treatment of Peat Water in Sarawak with Copper Electrodes." International Journal of Integrated Engineering, vol. 13, no. 12, 168-176, 2021.
https://doi.org/10.30880/ijie.2021.13.02.019
[8] I. G. Wenten, K. Khoiruddin, A. K. Wardani, P. T. P. Aryanti, D. I. Astuti, and A. A. I. A. S. Komaladewi. "Preparation of antifouling polypropylene/ZnO composite hollow fiber membrane by dip-coating method for peat water treatment." Journal of Water Process Engineering, vol. 34, p. 101158, 2020.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101158
[9] S. Kumari and R.N. Kumar. "River water treatment using electrocoagulation for removal of acetaminophen and natural organic matter." Chemosphere, vol. 273, p. 128571, 2021.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128571
[10] T. Ntambwe Kambuyi, R. Lamhar, Z. Zmirli, B. Bejjany, A. Aguelmous, H. Chaair, K. Digua, and A. Dani. "Hydrodynamic modelling and performance assessment of continuous-flow single-channel reactor for river water turbidity removal using electrocoagulation process." Chemical Engineering Research and Design, vol. 197, pp. 496-50, 2023.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2023.08.003
[11] A. Tahreen, M. S. Jami, and F. Ali. "Role of electrocoagulation in wastewater treatment: A developmental review." Journal of Water Process Engineering, vol. 37, p. 101440, 2020.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101440
[12] A. Shokri and B. Nasernejad. "Electrocoagulation process for spent caustic treatment: Optimization, sludge analysis and economic studies." Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, vol. 135, pp. 471-479, 2024.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2024.01.058
[13] A. A. Sari, N. Suwanto, A. A. Asmara, N. Ariani, A. A. R. Setiawan, J. Waluyo, Muryanto, and Sudarno. "Performance evaluation and operation cost analysis of electrolytes application in electrocoagulation process applied to peat wastewater treatment." AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 2175, p. 020038, 2019.
https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5134602
[14] Y. Mao, S. Cotterill, D. Morgan, S. Regan, and Y. Zhao. "Electrocoagulation of peatland runoff: Statistical optimization and economic analysis." Journal of Water Process Engineering, vol. 49, p. 103113, 2022.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.103113
[15] N. A. Rahman, C. J. Jol, A. A. Linus, and V. Ismail. "Emerging Application of Electrocoagulation for Tropical Peat Water Treatment: A Review." Chemical Engineering and Processing - Process Intensification, vol. 165, p. 108449, 2021.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2021.108449
[16] S. Snehi, H. Singh, T. Priya, and B. K. Mishra. "Understanding the natural organic matter removal mechanism from mine and surface water through the electrocoagulation method." Journal of Water Supply: Research and Technology-Aqua, vol. 68, no. 7, pp. 523-534, 2019.
https://doi.org/10.2166/aqua.2019.167
[17] S. T. McBeath, A. Nouri-Khorasani, M. Mohseni, and D. P. Wilkinson. "In-situ determination of current density distribution and fluid modeling of an electrocoagulation process and its effects on natural organic matter removal for drinking water treatment." Water Research 171, vol. 171, p. 115404, 2020.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.115404
[18] A. El-Ghenymy, M. Alsheyab, A. Khodary, I. Sirés, and A. Abdel-Wahab. "Corrosion behavior of pure titanium anodes in saline medium and their performance for humic acid removal by electrocoagulation." Chemosphere, vol. 246, p. 125674, 2020.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125674
[19] G. Hasani, A. Maleki, H. Daraei, R. Ghanbari, M. Safari, G. McKay, K. Yetilmezsoy, F. Ilhan, and N. Marzban. "A comparative optimization and performance analysis of four different electrocoagulation-flotation processes for humic acid removal from aqueous solutions." Process Safety and Environmental Protection, vol. 121, pp. 103-117, 2019.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2018.10.025
[21] M. Ebba, P. Asaithambi, and E. Alemayehu. "Development of electrocoagulation process for wastewater treatment: optimization by response surface methodology." Heliyon, vol. 8, no. 5, p. e09383, 2022.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09383
[22] S. J. S. Chelladurai, K. Murugan, A.P. Ray, M. Upadhyaya, V. Narasimharaj, and S. Gnanasekaran. "Optimization of process parameters using response surface methodology: A review." Materials Today: Proceedings, vol. 37, no. 2, pp. 1301-1304, 2021.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.06.466
[23] S. Oza, P. Kodgire, and S.S. Kachhwaha. "Analysis of RSM Based BBD and CCD Techniques Applied for Biodiesel Production from Waste Cotton-Seed Cooking Oil via Ultrasound Method." Analytical Chemistry Letters, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 86-101, 2022.
https://doi.org/10.1080/22297928.2021.2019611
[24] T. Rangseesuriyachai, K. Pinpatthanapong, J. Boonnorat, S. Jitpinit, T. Pinpatthanapong, and T. Mueansichai. "Optimization of COD and TDS removal from high-strength hospital wastewater by electrocoagulation using aluminium and iron electrodes: Insights from central composite design." Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, vol. 12, no. 1, p. 111627, 2024.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2023.111627
[25] P. C. Ulfa, A. Mirwan, D. R. Wicakso, S. Sahrani, A. F. Azwari, L. H. Lestarif, and N. Maliyah. "Influence of Current Density for Pollutant Removal from Palm Oil Mill Effluent." Advances in Science and Technology, vol. 138, pp. 105-111. 2024.
https://doi.org/10.4028/p-8RGeN8
[26] F. I. B. Ogando, C. L. de Aguiar, J. V. N. Viotto, F. J. Heredia, and D. Hernanz. "Removal of phenolic, turbidity and color in sugarcane juice by electrocoagulation as a sulfur-free process." Food Research International, vol. 122, pp. 643-652, 2019.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2019.01.039
[27] C. C. D. Thai, L. Moghaddam, and W. O. S. Doherty. "The influence of impurities on calcium phosphate floc structure and size in sugar solutions." Journal of Food Engineering, vol. 181, pp. 20-27, 2016.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Agus Mirwan, Sheilvina Milliviyanthi Dessy, Doni Rahmat Wicakso, Bella Febrianty Putri Suherman, Siti Nurhalisa

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.