Quercetin Encapsulation on Chitosan-Pectin Membranes as a Drug Delivery and Its Release Kinetics
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55981/jsmi.2025.9988Keywords:
Chitosan, pectin, polyelectrolyte complex, QuercetinAbstract
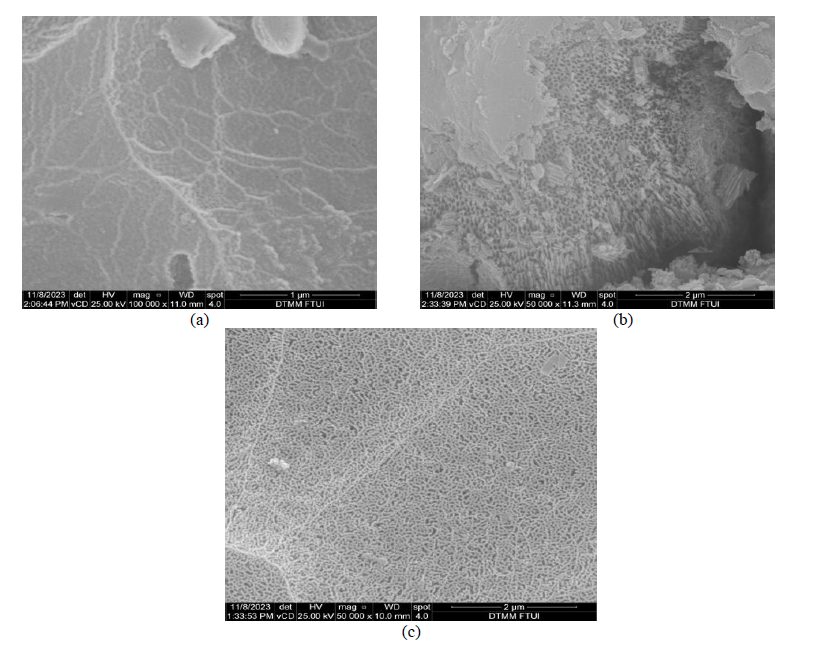
Chitosan-pectin membranes are biodegradable polyelectrolyte complexes, derived from biomaterials, with good stability for drug delivery applications. This study investigates the potential of these membranes to encapsulate quercetin, a flavonoid known for its therapeutic properties but limited for its low solubility, poor bioavailability, and rapid elimination. The membranes were synthesized using a 1:1 (w/w) chitosan-to-pectin ratio and loaded with quercetin via solvent evaporation. Characterization using FTIR confirmed the presence of OH, C=O, and NH groups; XRD indicated semi-crystalline structure; and SEM revealed a uniform, porous morphology. The maximum quercetin loading efficiency reached 82.43%, with the highest release (90.39%) observed at pH 1.2, following first-order kinetics. The resulting membrane was thin, brown, homogeneous, and tear-resistant, demonstrating its potential as a controlled drug delivery matrix for quercetin
Downloads
References
[1] A. F. Almeida et al., “Bioavailability of Quercetin in Humans with a Focus on Interindividual Variation.," Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science And Food Safety, vol. 17, no. 3, pp. 714–731, 2018, doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12342.
[2] D. Xu, M. J. Hu, Y. Q. Wang, and Y. L. Cui, “Antioxidant Activities of Quercetin and Its Complexes for Medicinal Application,” Molecules, vol. 24, no. 6, 2019, doi: 10.3390/molecules24061123.
[3] G. El-Saber Batiha et al., “The Pharmacological Activity, Biochemical Properties, And Pharmacokinetics Of The Major Natural Polyphenolic Flavonoid: Quercetin,” Foods, vol. 9, no. 3, 2020, doi: 10.3390/foods9030374.
[4] A. J. Vargas and R. Burd, “Hormesis and Synergy: Pathways and Mechanisms of Quercetin in Cancer Prevention and Management,” Nutrtion Reviews., vol. 68, no. 7, pp. 418–428, 2010, doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.2010.00301.x.
[5] K. M. Krishna et al., “Partial Reversal by Rutin and Quercetin of Impaired Cardiac Function in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats,” Canadian journal of physiology and pharmacology, vol. 83, no. 4, pp. 343–355, 2005, doi: 10.1139/y05-009.
[6] J. Maciej et al., “Bioavailability of the flavonol Quercetin in Neonatal Calves After Oral Administration of Quercetin Aglycone or Rutin,” Journal of dairy science, vol. 98, no. 6, pp. 3906–3917, 2015, doi: 10.3168/jds.2015-9361.
[7] G. T. Rich, M. Buchweitz, M. S. Winterbone, P. A. Kroon, and P. J. Wilde, “Towards an Understanding of the Low Bioavailability of Quercetin: A Study of Its Interaction with Intestinal Lipids.,” Nutrients, vol. 9, no. 2, 2017, doi: 10.3390/nu9020111.
[8] H. Patel, D. R. Panchal, U. Patel, T. Brahmbhatt, and M. Suthar, “Matrix Type Drug Delivery System : A Review,” Journal of Pharmaceutical Science and Bioscientific Research (JPSBR), vol. 1, no. 3, pp. 143–151, 2011.
[9] G. Tiwari et al., “Drug Delivery Systems: An Updated Review.,” International Journal of Pharmaceutical investigation, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 2–11, 2012, doi: 10.4103/2230-973X.96920.
[10] G. F. Oliveira, P. C. Ferrari, L. Q. Carvalho, and R. C. Evangelista, “Chitosan-Pectin Multiparticulate Systems Associated with Enteric Polymers for Colonic Drug Delivery,” Carbohydrate Polymers, vol. 82, no. 3, pp. 1004–1009, 2010, doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.06.041.
[11] M. R. I. Shishir, N. Karim, V. Gowd, J. Xie, X. Zheng, and W. Chen, “Pectin-Chitosan Conjugated Nanoliposome as a Promising Delivery System for Neohesperidin: Characterization, Release Behavior, Cellular Uptake, and Antioxidant roperty,” Food Hydrocolloids, vol. 95, pp. 432–444, 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.04.059.
[12] M. George and T. E. Abraham, “Polyionic Hydrocolloids for The Intestinal Delivery of Protein Drugs: Alginate and Chitosan- a Review.,” Journal of controlled release : official journal of the Controlled Release Society, vol. 114, no. 1, pp. 1–14, 2006, doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2006.04.017.
[13] F. Bigucci, B. Luppi, L. Monaco, T. Cerchiara, and V. Zecchi, “Pectin-Based Microspheres for Colon-Specific Delivery of Vancomycin.,” The Journal of pharmacy and pharmacology, vol. 61, no. 1, pp. 41–46, 2009, doi: 10.1211/jpp/61.01.0006.
[14] J. M. Joel, J. Barminas, E. Y. Riki, J. Yelwa, and E. Friday," Extraction and Characterization of Hydrocolloid Pectin from Goron Tula (Azanza garckeana) fruit, " World Scientific News, pp. 157–171, 2018.
[15] A. S. Soubhagya, A. Moorthi, and M. Prabaharan, “Preparation and Characterization of Chitosan/Pectin/ZnO Porous Films for Wound Healing,” International journal of biological macromolecules, vol. 157, pp. 135–145, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.04.156.
[16] I. C. C. M. Porto, T. G. Nascimento, J. M. S. Oliveira, P. H. Freitas, A. Haimeur, and R. França, “Use of Polyphenols as a Strategy to Prevent Bond Degradation in The Dentin-Resin Interface.,” European journal of oral sciences, vol. 126, no. 2, pp. 146–158, Apr. 2018, doi: 10.1111/eos.12403.
[17] A. B. D. Nandiyanto, R. Oktiani, and R. Ragadhita, “How to Read and Interpret FTIR Spectroscope of Organic Material,” Indonesian Journal of Science and Technology, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 97–118, 2019, doi: 10.17509/ijost.v4i1.15806.
[18] P. Mukhopadhyay, S. Maity, S. Chakraborty, R. Rudra, H. Ghodadara, M. Solanki, A.S. Chakraborti, A.K Prajapati “Oral Delivery of Quercetin to Diabetic Animals Using Novel pH Responsive Carboxypropionylated Chitosan/Alginate Microparticles,” RSC Advances, vol. 6, no. 77, pp. 73210–73221, 2016, doi: 10.1039/c6ra12491g.
[19] N. Q. Shi, Y. S. Lei, L. M. Song, J. Yao, X. B. Zhang, and X. L. Wang, “Impact of Amorphous and Semicrystalline Polymers on The Dissolution and Crystallization Inhibition of Pioglitazone Solid Dispersions,” Powder Technology, vol. 247, pp. 211–221, 2013, doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2013.06.039.
[20] P. H. Chen et al., “Novel Chitosan-Pectin Composite Membranes With Enhanced Strength, Hydrophilicity and Controllable Disintegration,” Carbohydrate Polymer, vol. 82, no. 4, pp. 1236–1242, 2010, doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.06.057.
[21] K. H. Ramteke, P. A. Dighe, A. R. Kharat, and S. V. Patil, “Mathematical Models of Drug Dissolution : A Review,” Journal of the Philosophy of Historya, vol. 3, no. 5, pp. 388–396, 2014.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Budi Hastuti, Saptono , Safarin Nisriyah, Mutiah Martanisa, Azlan Kamari

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.