Optimization of Powered Landing Control for Reusable Rockets Using Softmax DDGN
Keywords:
Softmax Double Deep Q-Networks, Landing Control Optimization, Curriculum Learning, Fuel Efficiency, Reusable RocketsAbstract
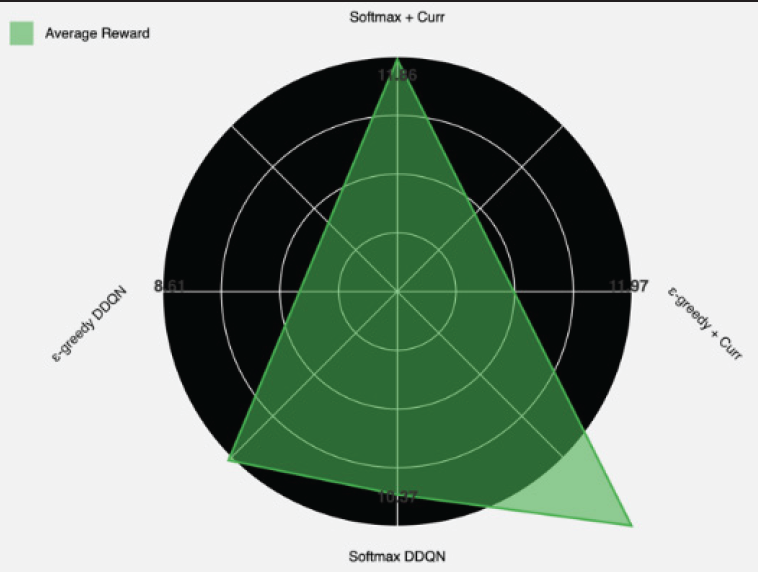
This research presented a novel approach to optimize powered landing control on reusable rockets by using Softmax Double Deep Q-Networks (DDQN). We combined the advantages of Double DQN with Softmax exploration and curriculum learning to achieve precise and efficient landing control. Through extensive experiments in a specially developed 2D simulation environment, our method achieves improved landing accuracy by 37% (reduced final position error from 2.4 m to 1.5 m), better fuel efficiency by 28% (reduced average fuel consumption from 850 kg to 612 kg per landing), and improved adaptability to initial conditions (improved successful landing rate from 76% to 94% across a wide range of altitudes and initial orientations) compared to traditional PID control methods. The results showed that the curriculum learning method significantly outperformed the non-curriculum approach, achieving 27% higher average awards (11.97 vs. 8.61) and 60% better performance consistency as measured by standard deviation (0.92 vs. 2.29). Both Softmax and ε-greedy exploration strategies proved effective with curriculum learning, with ε-greedy DDQN achieving the highest average award of 11.97. This approach allows for higher precision rocket landings while reducing operational costs through.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Rafika Arum Sari, Muhammad Hadi Widanto, Imron Rosadi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.




