Fuel Efficiency Comparison of PBN and ILS Approach Procedures at Sam Ratulangi Airport
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55981/ijoa.2024.8968Keywords:
pbn, ils, fuel efficiency, BlueSky Simulation, FlightRadar24, Sam Ratulangi International AirportAbstract
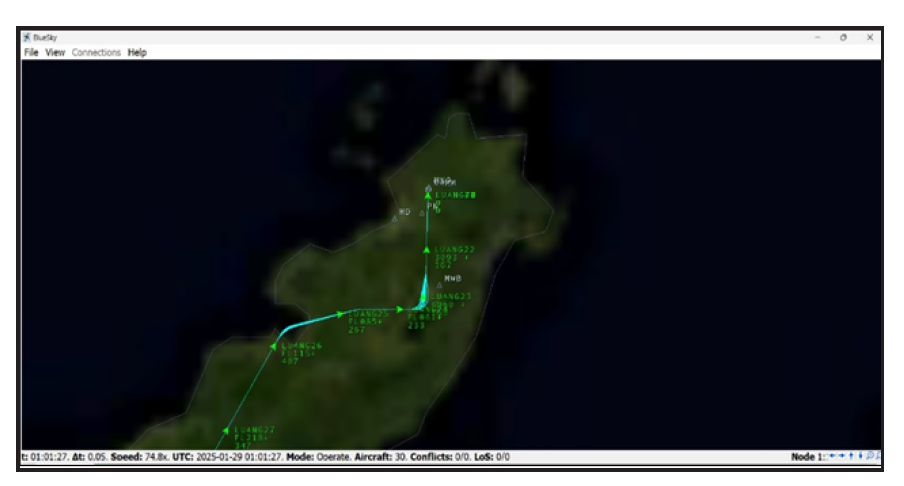
This study evaluates the efficiency of approach procedures at Sam Ratulangi International Airport-Manado by comparing Required Navigation Performance (RNP) under Performance-Based Navigation (PBN) with the Instrument Landing System (ILS) as a conventional procedure. A simulation using the BlueSky ATM Simulator was conducted with 30 aircraft instances for each approach, utilizing real-time FlightRadar24 speed data to ensure operational realism. The analysis focused on three key metrics: distance flown, time spent, and fuel consumption. Results show that implementing of PBN procedures reduces distance flown by 15%, flight time by 15% and fuel consumption by 14% compared to ILS, demonstrating improved operational efficiency. This research provides a quantitative assessment of PBN systems’ effectiveness in optimizing approach procedures, supporting aviation sustainability, and reducing operational costs.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Banni Yulia M'Azzuri, Toto Indriyanto, Javensius Sembiring

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.




