Assessment of Soil Loss Using RUSLE Method in Mrica Reservoir Catchment, Central Java, Indonesia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55981/limnotek.2023.2210Keywords:
Mrica reservoir, RUSLE, soil lossAbstract
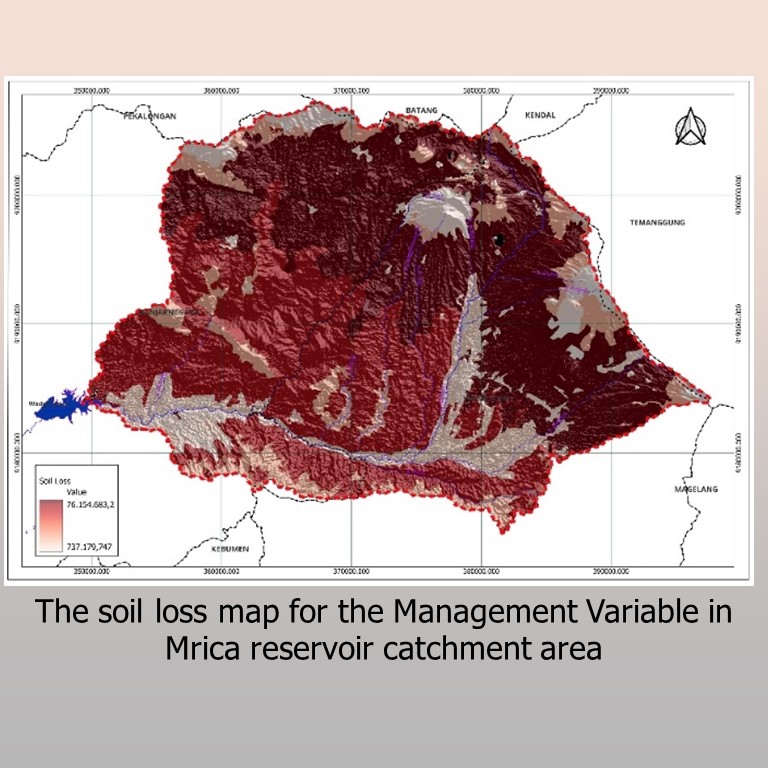
The Indonesian government has identified the Serayu Watershed as a priority area for restoration within the National Mid-Term Development Plan. One of the significant challenges in this region is the high level of soil erosion, which threatens the overall ecosystem. This study aims to estimate the amount of soil loss in the Mrica Catchment using the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) Method. Various data sources were utilized, including soil type, rainfall, land cover, Digital Elevation Model, and conservation data. Geographic Information System (GIS) techniques were employed to calculate the critical factors required by the RUSLE Method, including soil erodibility (K), rainfall erosivity (Ri), slope length and steepness factor (LS), and cover management and conservation factor (CP). This research provides critical information for land management in Mrica Catchment. These factors were used to estimate soil loss in the Mrica Catchment, revealing a range between 62,553 tons per year (t/y) and 21,323,311 t/y, with an average value of 443.90 ton per hectare per year (t/ha/y). These results indicate high erosion potential based on the Classification of Erosion Hazard (HER). This study provides critical information for land management and offers suggestions for devising effective strategies to mitigate sedimentation impact in the Serayu Watershed. The highest soil loss values according to the RUSLE Method, both under the Environmental and Management Variable, are observed in the same location, namely, in the north of Mrica Catchment. The findings emphasize the urgent need for erosion control measures and sustainable land management practices in this priority restoration area.
References
Abdul Rahaman, S., Aruchamy, S., Jegankumar, R., Abdul Ajeez, S., 2015. Estimation Of Annual Average Soil Loss, Based On Rusle Model In Kallar Watershed, Bhavani Basin, Tamil Nadu, India. ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information
Sciences II-2/W2, 207–214. DOI:10.5194/isprsannals-II-2-W2-207-2015
Abu Hammad, A., 2011. Watershed erosion risk assessment and management utilizing revised universal soil loss equation-geographic information systems in the Mediterranean
environments. Water and Environment Journal 25,
–162. DOI:10.1111/j.1747-6593.2009.00202.x
Ainun Jariyah, N., Budi Pramono, I., 2013. Kerentanan Sosial Ekonomi Dan Biofisik Di DAS Serayu: Collaborative Management. Jurnal
Penelitian Sosial dan Ekonomi Kehutanan 10, 141–156.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.20886/jpsek.2013.10. 3.141-156
Angima, S.D., Stott, D.E., O’Neill, M.K., Ong, C.K., Weesies, G.A., 2003. Soil erosion prediction using RUSLE for central Kenyan highland
conditions. Agric Ecosyst Environ 97, 295–308.
DOI:10.1016/S0167-8809(03)00011-2
Badan Informasi Geospasial, n.d. DEMNAS Seamless Digital Elevation Model (DEM) dan Batimetri Nasional [WWW Document]. URL
https://tanahair.indonesia.go.id/demnas/#/(accessed 7.1.23).
BAPPENAS, 2015. Kajian Pengaruh Kebijakan Konservasi Sumber Daya Air di dalam DAS Terhadap Sektor Kehutanan dan Sektor
lainnya.
Bizuwerk, A., Taddese, G., Getahun, Y., 2003. Application of GIS for modeling soil loss rate in Awash river basin, Ethiopia. International
Livestock Research Institute (ILRI), Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
Cantik, B.K.P., Legono, D., Rahardjo, A.P., 2021. Efektivitas Penggelontoran Sedimen (Flushing) Studi Kasus Waduk Pb Soedirman. Jurnal Teknik Sipil 16, 14–23. DOI:
https://doi.org/10.24002/jts.v16i1.4213
Chen, C.-N., Tsai, C.-H., 2017. Estimating Sediment Flushing Efficiency of a Shaft Spillway Pipe and Bed Evolution in a Reservoir. Water (Basel) 9, 924. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/w9120924
Christanto, N., Setiawan, M.A., Nurkholis, A., Istiqomah, S., Sartohadi, J., Hadi, M.P., 2018. Analisis Laju Sedimen DAS Serayu Hulu dengan
Menggunakan Model SWAT. Majalah Geografi Indonesia 32, 50.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.22146/mgi.32280
Eisenberg, J., Muvundja, F.A., 2020. Quantification of Erosion in Selected Catchment Areas of the Ruzizi River (DRC) Using the (R)USLE Model. Land (Basel) 9, 125. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/land9040125
Hanafi, F., Pamungkas, D., 2021. Aplikasi Model Rusle untuk Estimasi Kehilangan Tanah Bagian Hulu di Sub Das Garang, Jawa Tengah. Jurnal Geografi : Media Informasi Pengembangan dan Profesi Kegeografian 18, 30–36. DOI: https://doi.org/10.15294/jg.v18i1.28079
Koirala, P., Thakuri, S., Joshi, S., Chauhan, R., 2019. Estimation of Soil Erosion in Nepal Using a RUSLE Modeling and Geospatial Tool. Geosciences (Basel) 9, 147. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences9040147
Lembaga Kerjasama Fakultas Teknik UGM, 2015. Roadmap Pengelolaan Sedimentasi Waduk Mrica, Wadaslintang, Sempor di Wilayah Sungai Serayu Bogowonto.
Lesmana, S.B., 2020. Kajian Erosi Pada Sub Das Serayu Sebagai Daerah Tangkapan Air Waduk Mrica. Semesta Teknika 23, 182–186. URL https://journal.umy.ac.id/index.php/st/article/ view/12082 (accessed 8.1.23).
Morgan, R.P.C., Quinton, J.N., Smith, R.E., Govers, G., Poesen, J.W.A., Auerswald, K., Chisci, G., Torri, D., Styczen, M.E., 1998. The European Soil Erosion Model (EUROSEM): a dynamic approach for predicting sediment transport from fields and small catchments. Earth Surf Process Landf 23, 527–544. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)10969837(199806)23:6%3C527::AIDESP868%3E3.0.CO;2-5
Novico, F., Priohandono, Y.A., 2012. Analysis of Erosion and Sedimentation Patterns Using Software of Mike 21 HDFM-MT in The Kapuas Murung River Mouth Central KalimantanProvince. Bulletin of the Marine Geology 27, 35–53. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.32693/bomg.27.1.2012.44
Pambudi, A.S., Moersidik, S.S., Karuniasa, M., 2021. Analysis of Recent Erosion Hazard Levels and Conservation Policy Recommendations for Lesti Subwatershed, Upper Brantas Watershed. Jurnal Perencanaan Pembangunan: The Indonesian Journal of Development Planning 5, 71–93.
Panagos, P., Borrelli, P., Meusburger, K., van der Zanden, E.H., Poesen, J., Alewell, C., 2015. Modelling the effect of support practices (Pfactor) on the reduction of soil erosion by water at European scale. Environ Sci Policy 51, 23–34. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsci.2015.03.012
Renard, K.G., 1997. Predicting soil erosion by water: a guide to conservation planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE). US Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. URL DOI: https://doi.org/10.36574/jpp.v5i1.167 https://www.ars.usda.gov/arsuserfiles/64080530/rusle/ah_703.pdf (accessed 8.1.23).
Saputra, B., Mudjiatko, Rinaldi, 2020. Identifikasi Potensi Erosi dan Besar Sedimentasi pada DAS Kaiti. Jom FTEKNIK 7: 1–12. URL https://jom.unri.ac.id/index.php/JOMFTEKNIK/article/view/28435 (accessed 8.1.23).
Schwab, G.O., Fangmeier, D.D., Elliot, W.J., 1993. Soil and Water Conservation Engineering, 4th ed. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/S0021859600068611
Tian, P., Zhu, Z., Yue, Q., He, Y., Zhang, Z., Hao, F., Guo, W., Chen, L., Liu, M., 2021. Soil erosion assessment by RUSLE with improved P factor and its validation: Case study on mountainous and hilly areas of Hubei Province, China. International Soil and Water Conservation Research 9, 433–444. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2021.04.007
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 LIMNOTEK Perairan Darat Tropis di Indonesia

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






